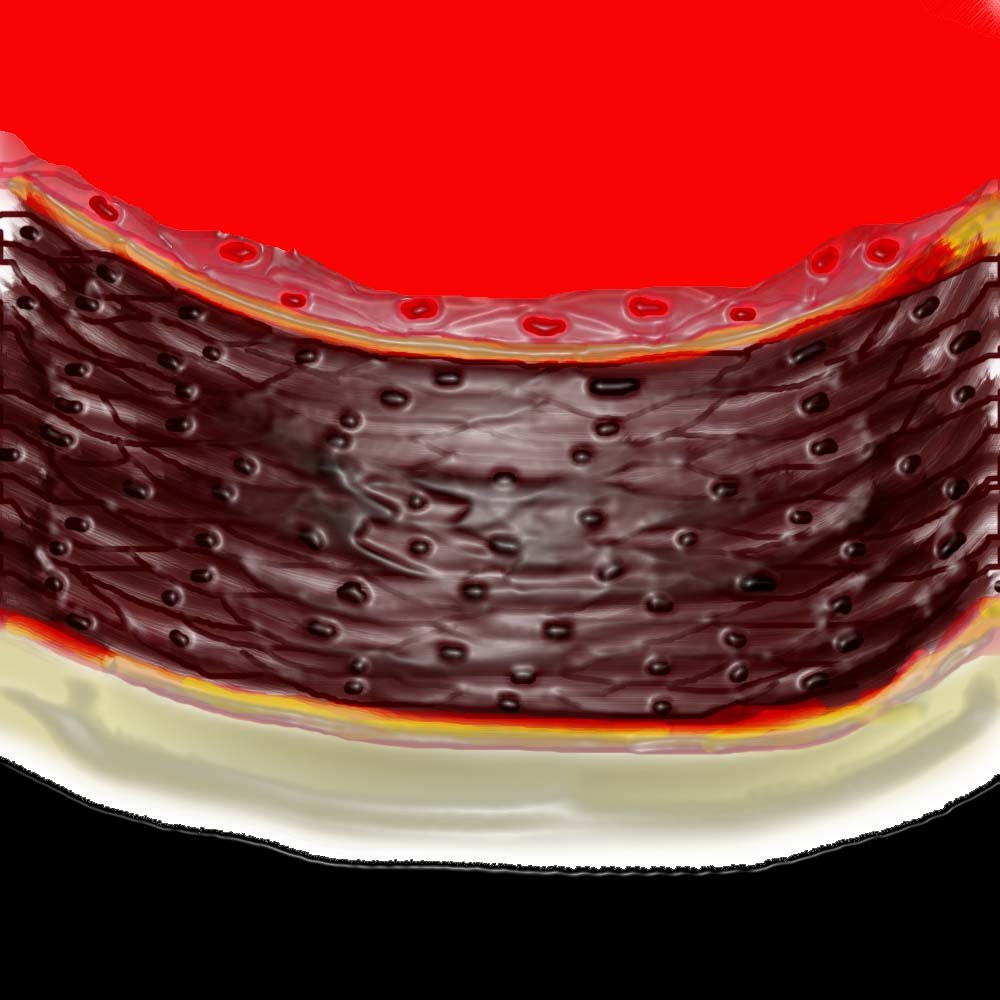

This artists representation of the normal muscular arterial wall consisting of three basic layers. The intima, media and adventitia.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33785

This artists representation of the normal muscular arterial wall consisting of three basic layers. The intima, media and adventitia.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33785b
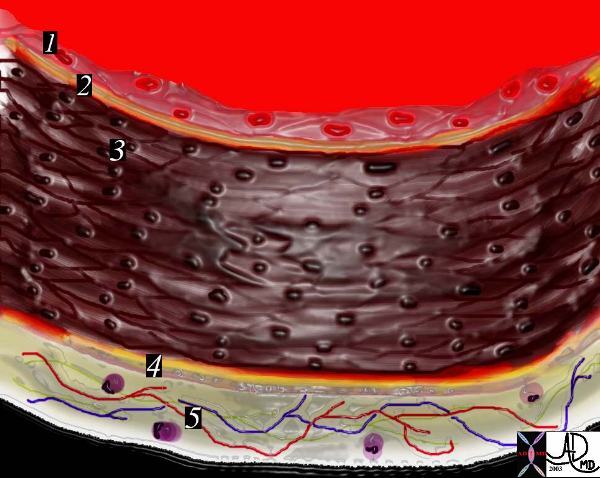
This is a diagram of a medium sized muscular artery. The lumen colored in red is lined by the intima (1 and 2)
A single layer of squamous epithelium called the endothelium (1), is supported by the connective tissue and the internal elastic membrane of the basal lamina (2).
The tunica media is made of smooth muscle(3) and the external elastic membrane (4).
Variable amounts of elastin proteoglycans, and reticular fibres are intermixed within the media. The tunica adventitia (5) is the outer layer and consists of longitudinally oriented collagenous fibres with some elastin and the vasa vasorum and lymphocytes.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33785c
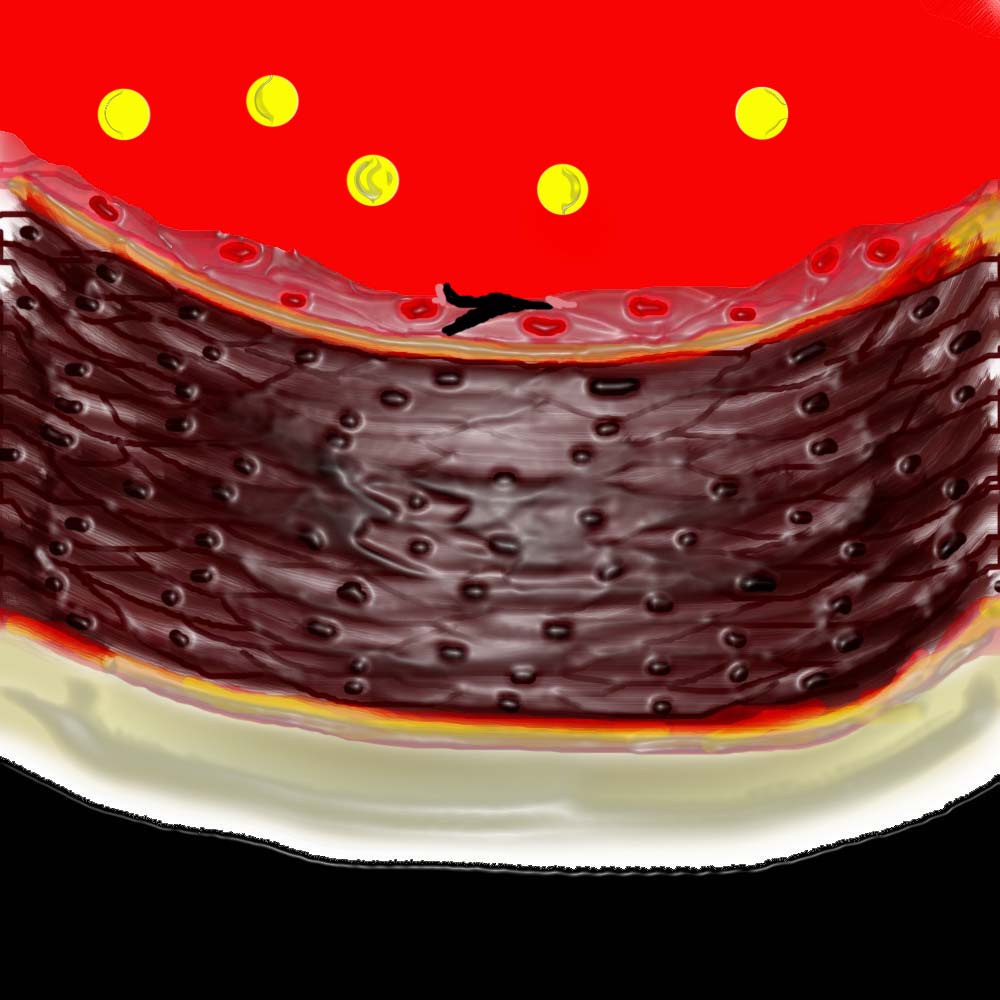

In the early stages of atherosclerosis there is intimal injury and a breach in the endothelium. Circulating phospholipids note in theblood.
vasorum capillaries circulating phospholipids intimal injury normal anatomy histology drawing art Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33790
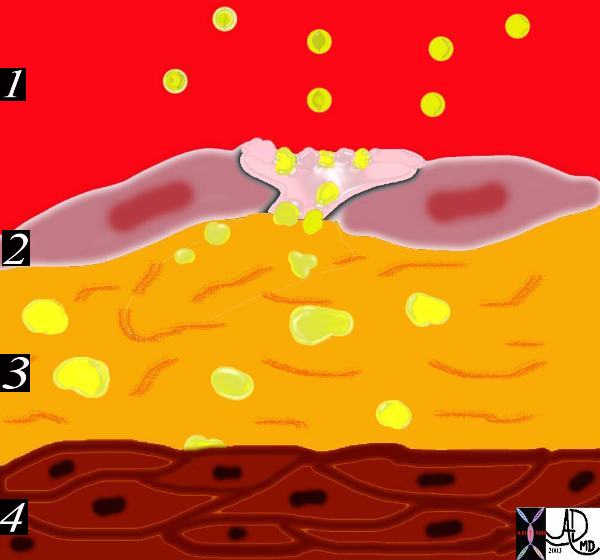
The circulating lipoproteins enter a breached endothelium (2) and enter the subendothelial layer of supporting connective tissue within which are linear starands of proteoglycan. (3). At this stage the media (4) is quiescent. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 33792d code heart artery intima endothelium histopathology pathogenesis atherosclerosis atheroma drawing Davidoff art
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
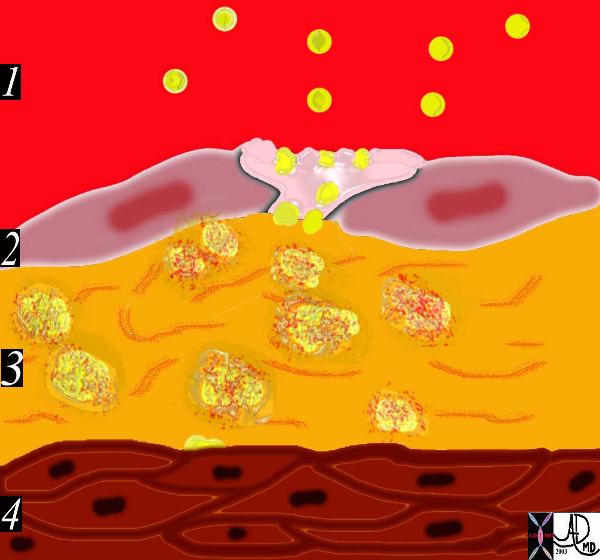
This diagram shows the yellow spheroidal lipoproteins traversing the injured epithelium (2) from the lumen (red) and binding to the linear shaped proteoglycan molecules in the intimal layer. (3) In essence the lipoprotein is “captured”, because it has been altered structurally and is unable to return to the circulation. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 33792e code heart artery intima endothelium histopathology pathogenesis atherosclerosis atheroma drawing Davidoff art
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
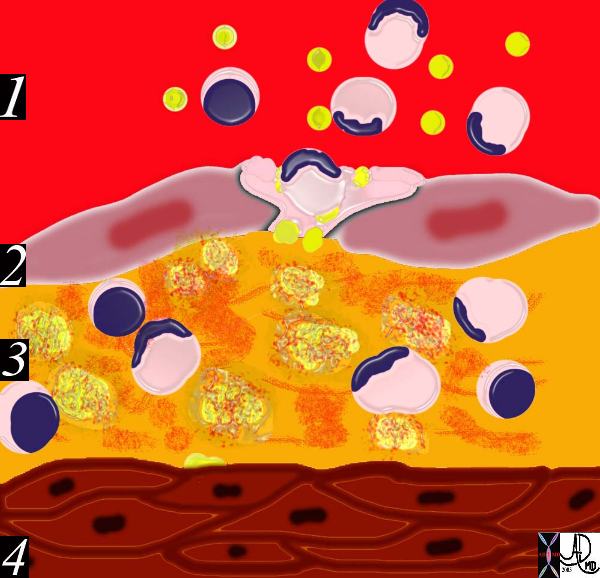
The diagram shows an evolving atheromatous plaque with inflammatory cells, monocytes, and lymphocytes infiltrating the intima which contains the lipoprotein- proteoglycan complex, extracellular lipid , and cholesterol crystals.
33792e
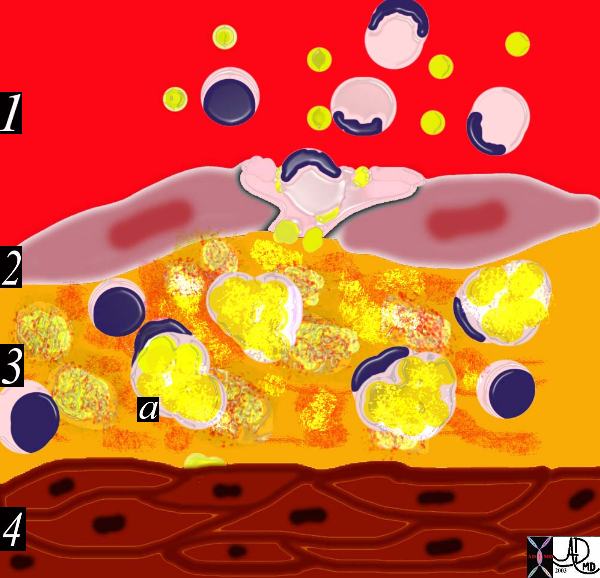
This drawing shows migration of the monocytes into the intima.
The monocytes transform into macrophages in the intima and phagocytose the lipid products to become lipid laden foamy cells.
The macroscopic correlate at this stage is the fatty streak.
2018
33792h
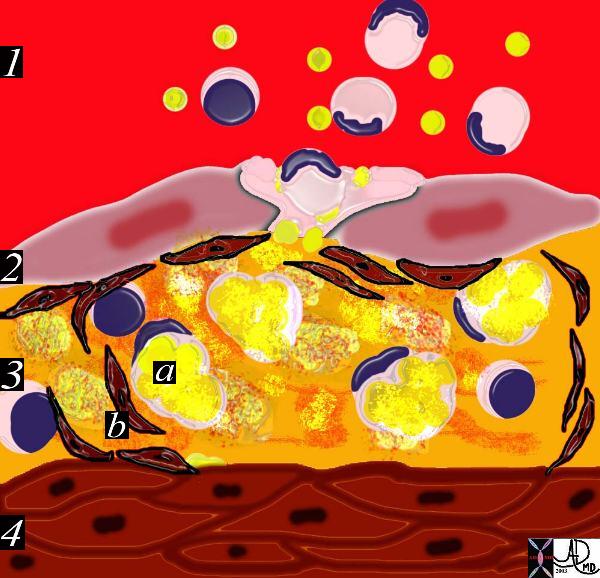
This diagram shows the reaction of the smooth muscle cells (b) to the formation of foam cells (a) in the subendothelial layer of the intima. The smooth muscle cells migrate from the muscular layer (4) into the intima. Here they undergo dedifferentiation into fibrocytes.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33792i
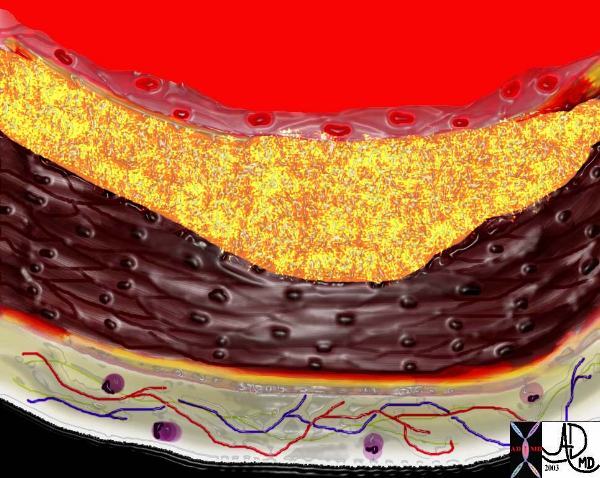
The diagram shows the atherosclerotic lesion in the subepithelial layer of the intima which at first bulges toward the media or muscular layer.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33801a
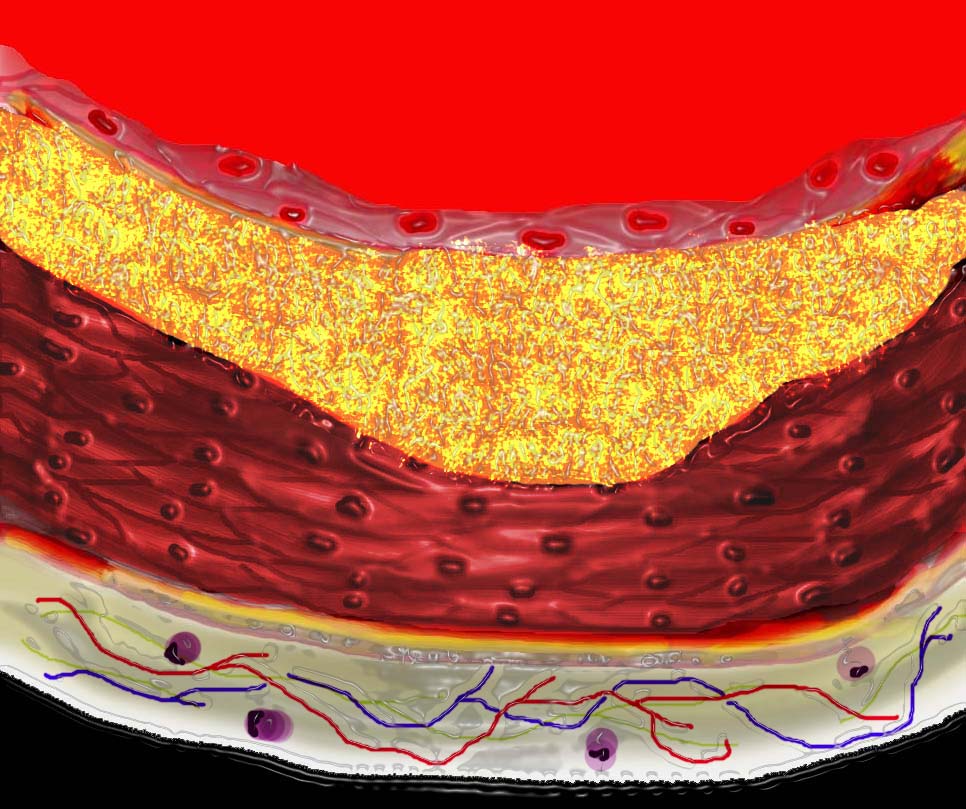
The diagram shows the atherosclerotic lesion in the subepithelial layer of the intima which at first bulges toward the media or muscular layer.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33801a01
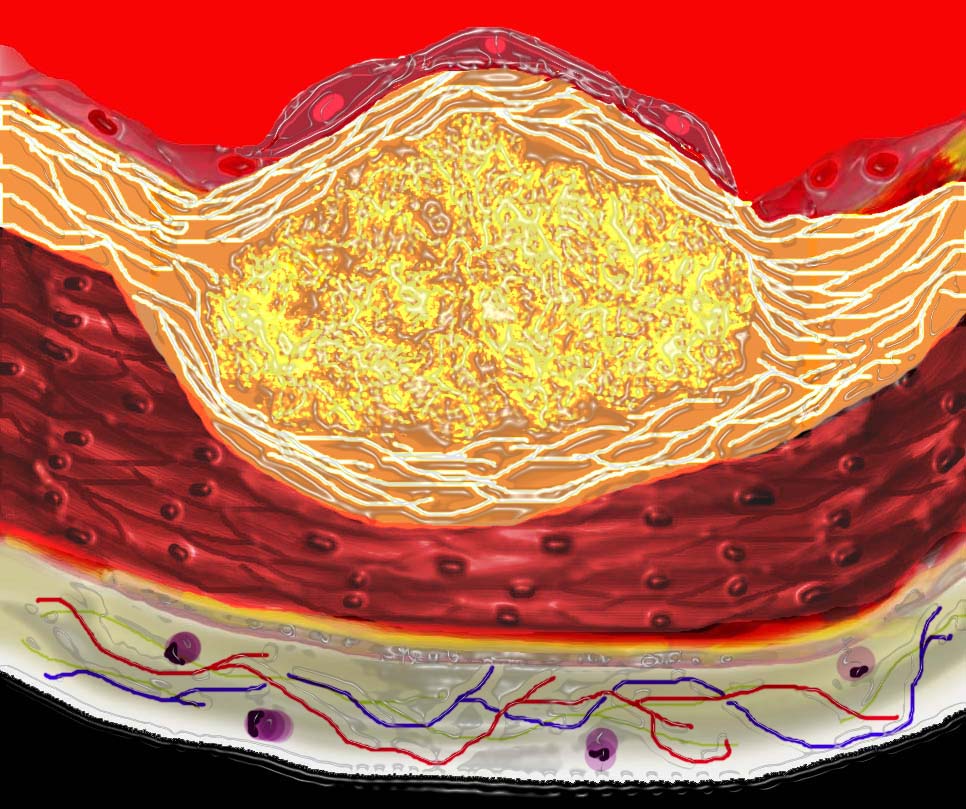
The diagram shows the atherosclerotic lesion in the subepithelial layer of the intima which is bulging both toward the media and toward the lumen. There is a central core of fat and necrotic debris, surrounded by fibrous elements which give the plaque its hardness to the feel.
The accumulation of fibrous tissue heralds an advanced atherosclerotic lesion.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33801b01
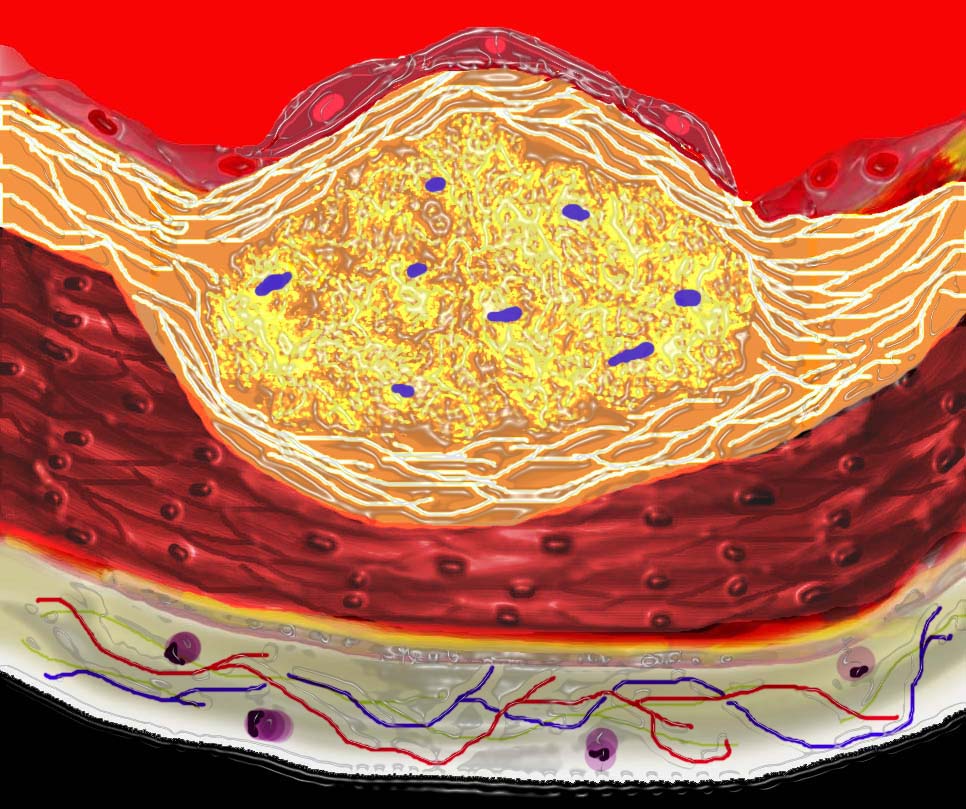
The diagram shows the atherosclerotic lesion in the subepithelial layer of the intima which is bulging both toward the media and toward the lumen. There is a central core of fat and necrotic debris, surrounded by fibrous elements which give the plaque its hardness to the feel.
The accumulation of fibrous tissue heralds an advanced atherosclerotic lesion.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33801b02
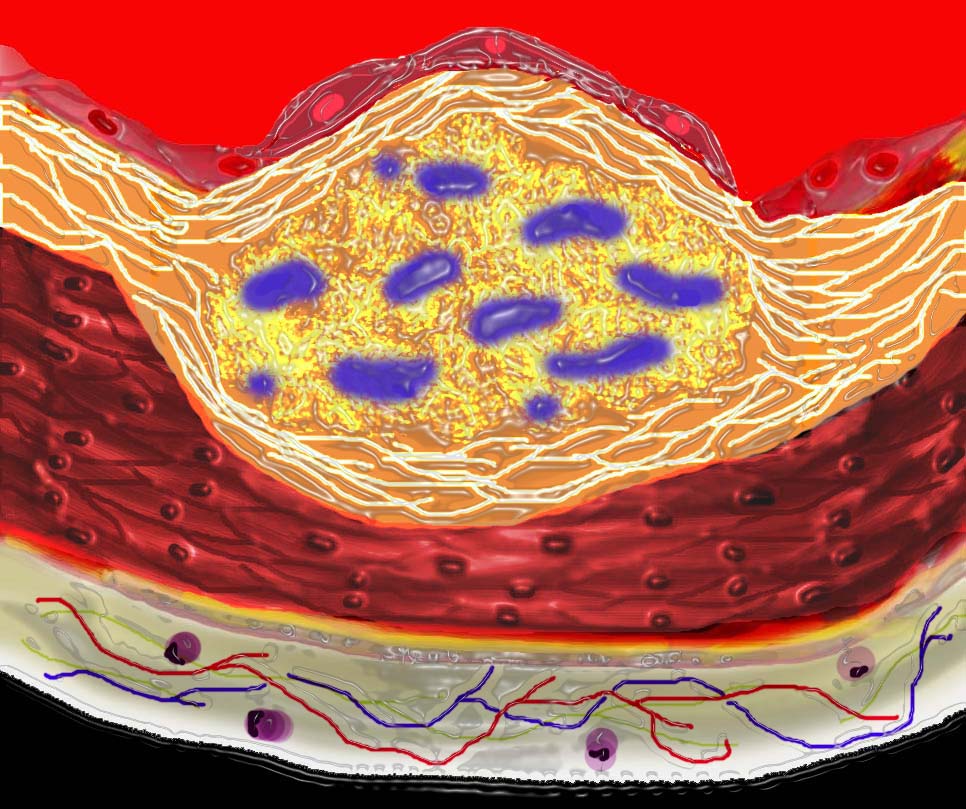
The diagram shows the atherosclerotic lesion in the subepithelial layer of the intima which is bulging both toward the media and toward the lumen. There is a central core of fat and necrotic debris, surrounded by fibrous elements which give the plaque its hardness to the feel.
The accumulation of fibrous tissue heralds an advanced atherosclerotic lesion.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33801b03

The diagram shows the atherosclerotic lesion in the subepithelial layer of the intima which is bulging both toward the media and toward the lumen. There is a central core of fat and necrotic debris, surrounded by fibrous elements which give the plaque its hardness to the feel.
The accumulation of fibrous tissue heralds an advanced atherosclerotic lesion.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33801b04

The diagram shows the atherosclerotic lesion in the subepithelial layer of the intima which is bulging both toward the media and toward the lumen. There is a central core of fat and necrotic debris, surrounded by fibrous elements which give the plaque its hardness to the feel.
The accumulation of fibrous tissue heralds an advanced atherosclerotic lesion.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33801b0
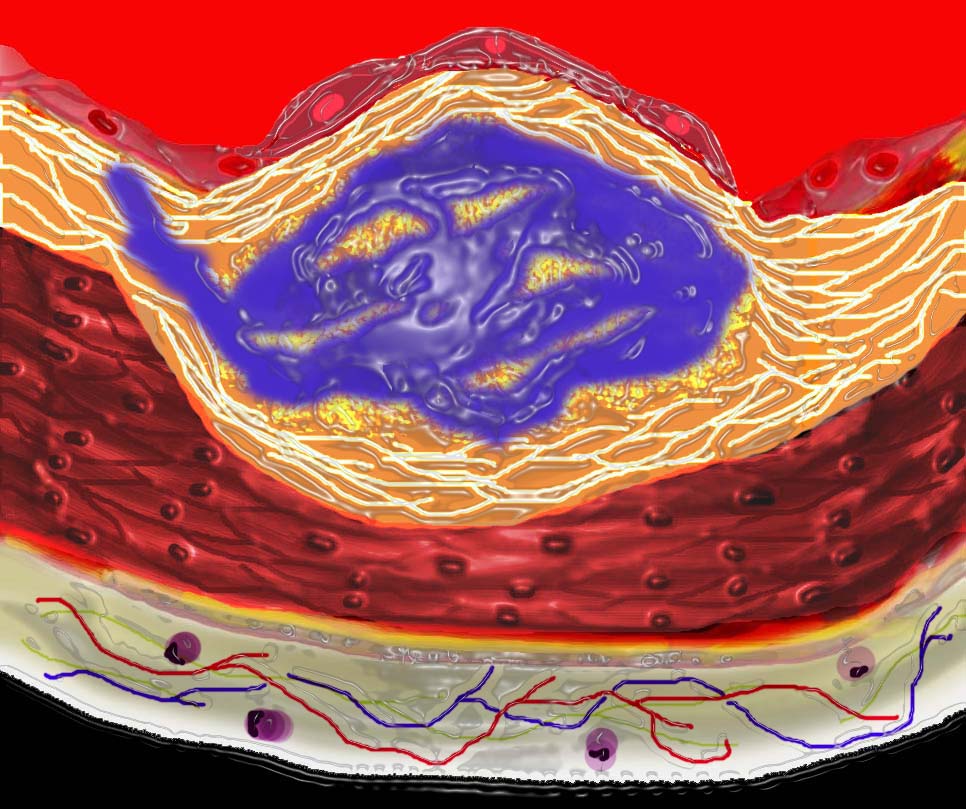
The diagram shows the atherosclerotic lesion in the subepithelial layer of the intima which is bulging both toward the media and toward the lumen. There is a central core of fat and necrotic debris, surrounded by fibrous elements which give the plaque its hardness to the feel.
The accumulation of fibrous tissue heralds an advanced atherosclerotic lesion.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33801b06
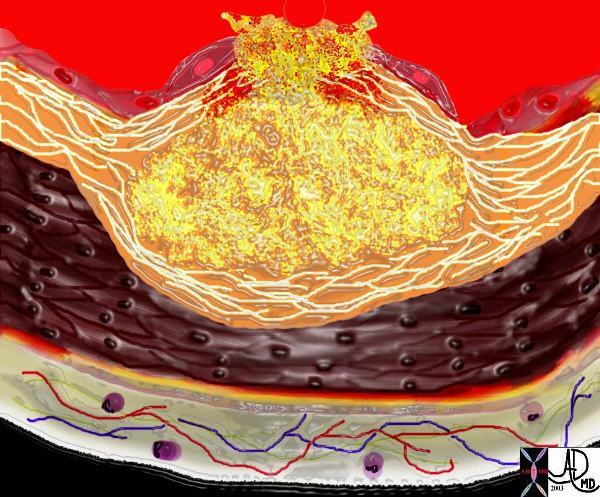
This diagram shows denudation of the endothelial layer with exposure and rupture of the contents of the atherosclerotic plaque in volcanic fashion into the lumen. This event is catastrophic and can result in acute thrombosis and may even be a fatal event. 33801d01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. code heart artery atherosclerosis atheroma vulnerable plaque drawing Davidoff art
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
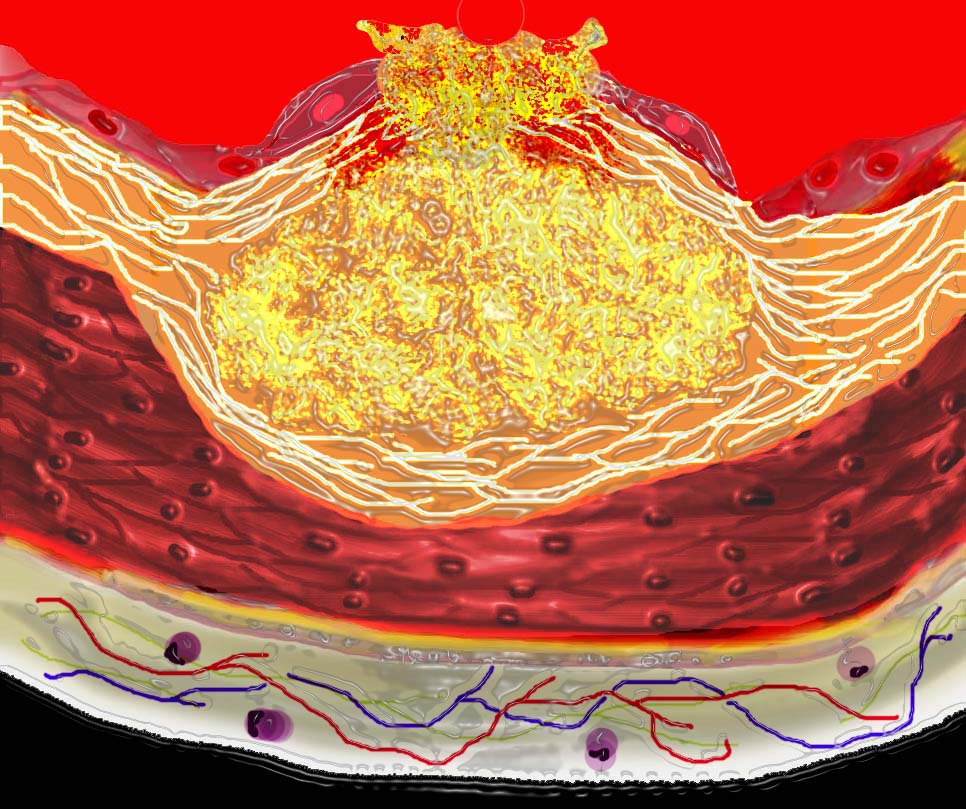
This event is catastrophic and can result in acute thrombosis and may even be a fatal event.
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33801d01
Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2018
33803